What Is A Market Failure?
In Economics, market failure is a situation in which the allocation of goods and services by a free market is not efficient, leading to a net loss of economic value.
There are 6 market failures:
1. Creation of Externalities
An externality is a cost or benefit for a third party who did not agree to it. There are:
Positive externalities – education, healthcare ( if we left to the market, it would underproduce)
Negative externalities – tobacco, cars ( if we left to the market, it would overproduce)
2. Missing Markets – street lights, traffic lights ( ( if we left to the market, it would underproduce)
3. Asymmetric Knowledge – This is where there is a large difference between the knowledge of the buyer and the seller. The seller exploits the buyer and has him pay more than he should for the service: lawyers, doctors are good examples of asymmetrical knowledge market failure.
4. Lack of Competition – monopolies, oligopolies.
5. Unstable Prices – commodity prices, fossil fuels. All these price fluctuations affect society in general.
6. Labor Market Failure – in relation to wages and demand for labor. Especially in a situation where the worker is more qualified in proportion to the wage received.
Imposed Costs
To understand externalities, we need to understand the costs associated with it. It comes down to the following:
Social Cost = Private Cost + External Cost
A Private cost is the price paid by an individual or firm for a product or service.
An External Cost is an Externality – the healthcare bill imposed in form of taxes.
Positive Production Externalities
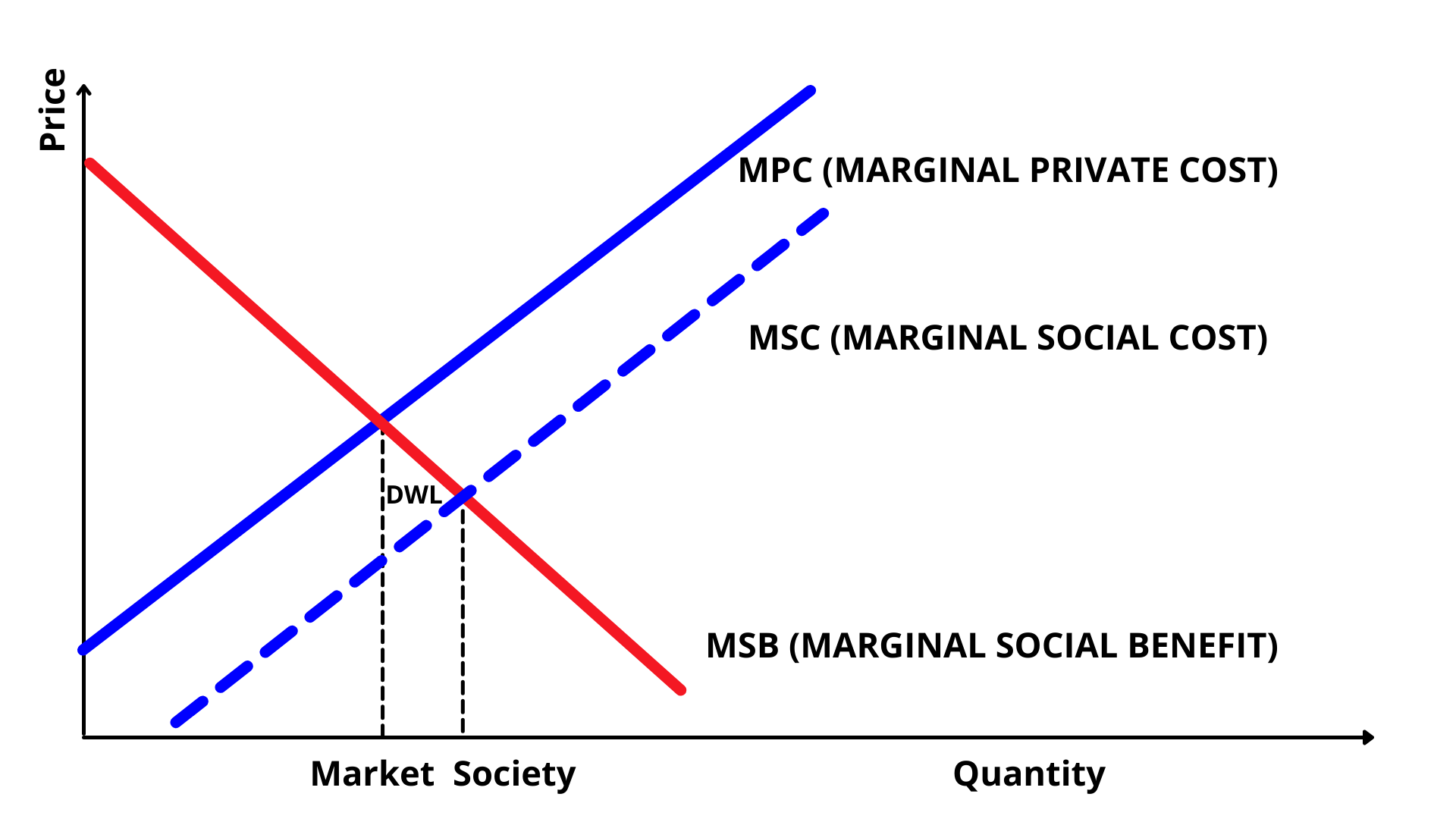
A Positive Production Externality example is local construction.
The construction of new local businesses may increase the value of local properties – which can create a positive benefit to local residents. This also creates jobs that provide income to residents, which can then further stimulate economic activity in that area. In turn, local residents benefit even if they do not use such a business.
Negative Production Externalities
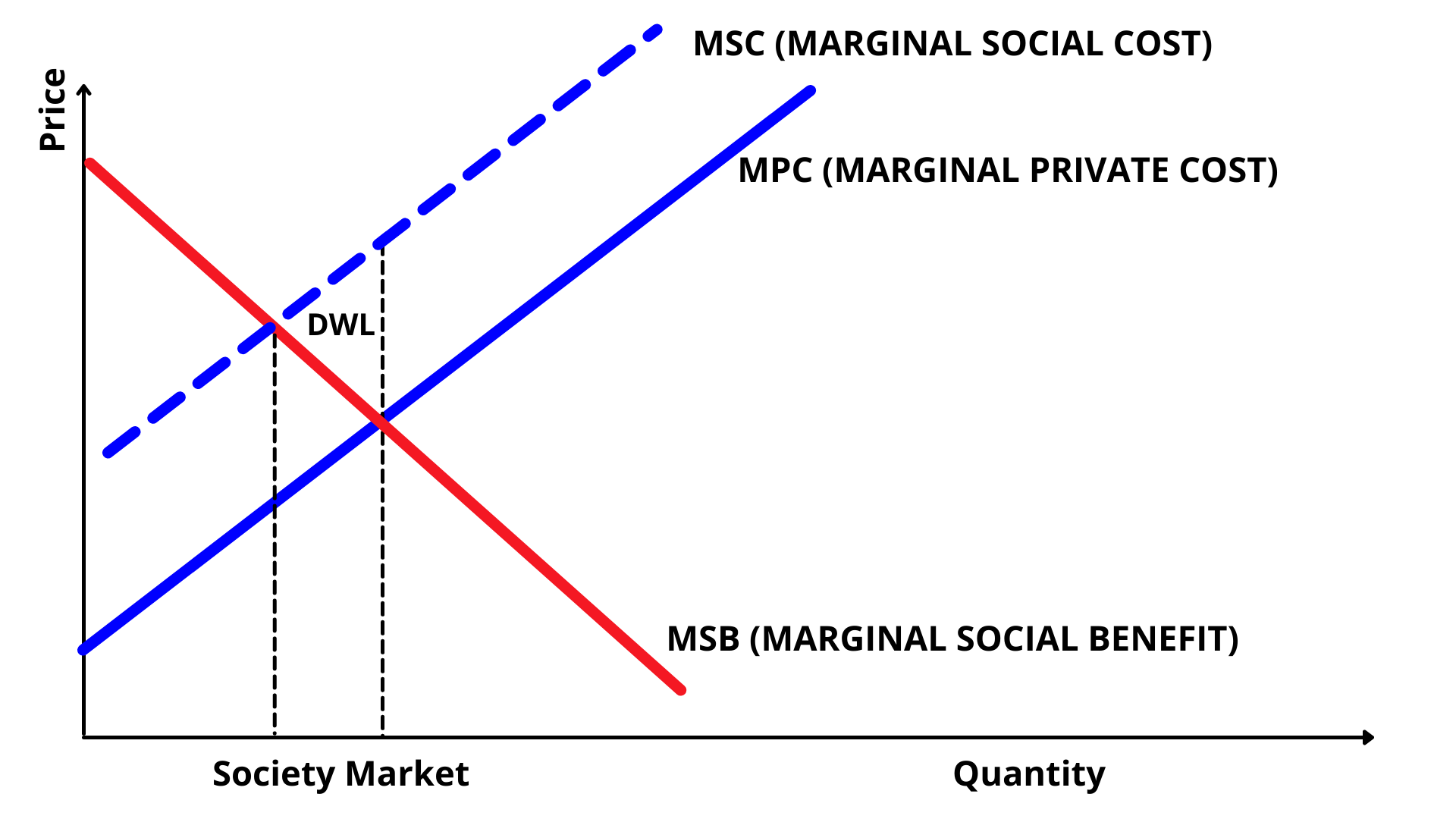
A Negative Production Externality example is air Pollution.
Factory emissions are the result of product production but have the byproduct of being a negative production externality has it has an impact on people’s health.
Positive Consumption Externalities

A Positive Consumption Externality example is advertising.
You are able to use a service like YouTube or Facebook for free, because someone else is paying YouTube to place ads. Ad Revenue is how YouTube makes money.
Negative Consumption Externalities
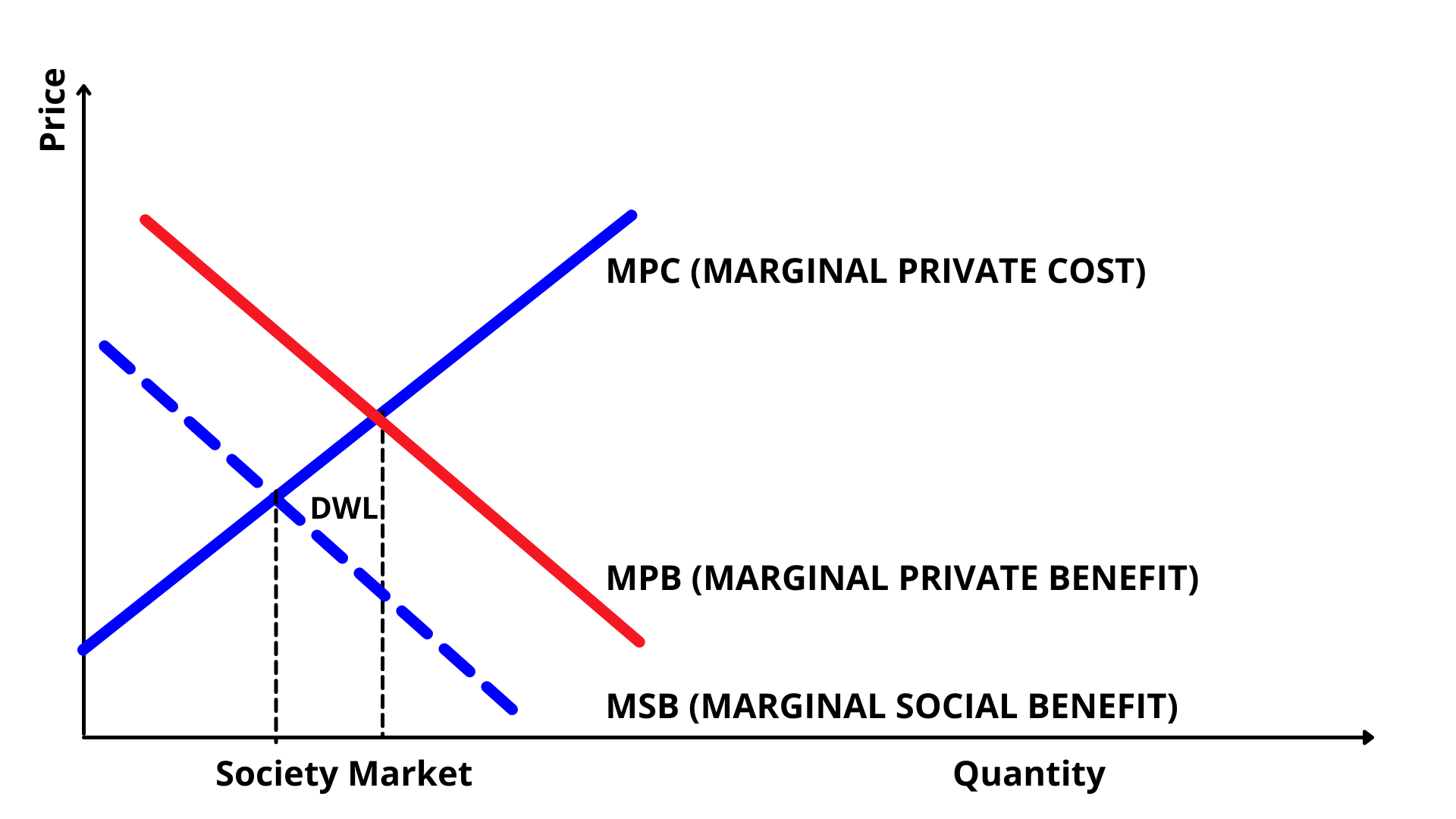
A Negative Consumption Externality example consumer behaviour that has economic consequences on society, like obesity, smoking or drinking. People that are obese, or smoke or have a drinking problem pose an economic social liability has public healthcare bills are paid by all in form of taxes.


